New Labour Law in India has brought major transformations to how workplaces operate across the country. In recent years, the government consolidated multiple outdated and complicated labour regulations into four simplified labour codes. These codes aim to make compliance easier for employers while ensuring better protection, transparency, and rights for employees. The new structure affects almost every business—whether it’s a small shop, a factory, an office, a startup, a gig-based company, or a large enterprise. With these reforms, India aims to create a more organised and fair working environment for everyone.
The changes brought by these laws touch on various aspects, including working hours, salaries, overtime, leave entitlements, appointment letters, social security, workplace safety, and digital record-keeping. Many businesses are already in the process of updating their HR systems to comply with the new rules.
This all-inclusive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the new labour law in India, using simple English and featuring expanded sections, examples, impacts, FAQs, and downloadable materials.
What Are the New Labour Law in India?
The four new Labour Law are:
- Code on Wages, 2019
- Industrial Relations Code, 2020
- Occupational Safety, Health & Working Conditions (OSH) Code, 2020
- Code on Social Security, 2020
Each code zeroes in on a specific area of employment, covering everything from wages to safety to social security.
1. Code on Wages, 2019
This law replaces four old wage laws and establishes a simplified system for the payment of salaries.
Key Features:
- Minimum wages prevail throughout the country.
- Equality in pay for equal work for all genders.
- Standard definition of “Wages” across industries.
- Salaries are to be paid on time, be it daily, weekly, or monthly.
- Deductions can’t exceed 50% of wages.
Why this matters:
Earlier, different laws defined wages differently, and it led to a lot of confusion regarding PF, ESI, and allowances. Now, there will be one definition that every firm will have to apply, and, thereby, payroll will also be more transparent.
2. Industrial Relations Code, 2020
It focuses on job security, the rights of workers, and how well employers and employees understand each other.
Key Features:
- Public notice of strikes in advance:
- Clear rules for layoffs and retrenchment.
- Easier for companies to hire contract workers legally.
- Mandatory grievance redressal committees for firms with more than 20 employees.
- More formalized rules for union formation.
Impact:
The code encourages fair communication and reduces conflicts inside workplaces.
3. Social Security Code, 2020
Because this code extends social security benefits to gig workers, platform workers, unorganized workers, and contract workers, it is one of the biggest reforms.
Key Features:
- PF, ESI, maternity benefits, gratuity, and disability benefits extended.
- Compulsory social security funds for gig workers.
- Companies shall pay contributions to social security schemes.
- Welfare schemes for unorganized sector workers.
Impact:
This will provide formal social protection to millions of delivery partners, drivers, freelancers, and small workers.
4. OSHWC Code, 2020 (Safety & Working Conditions)
This code focuses on the creation of safe, clean, and employee-friendly workplaces.
Key Features:
- Clear rules concerning working hours.
- Safety rules for hazardous industries.
- Women are allowed to work at night with security.
- Compulsory bathroom, drinking water, and first-aid facilities.
- Annual medical check-ups are necessary.
Impact:
Better hygiene, safer workplaces, and improved employee comfort.
Key Changes Under the New Labour Law in India
The New Labour Codes dealing with Wages, Industrial Relations, Social Security, and OSH (Safety & Working Conditions) bring the most far-reaching changes to India’s labour system in decades. The changes also aim at easing compliance for businesses and increasing protection for workers.
Below are the major changes explained in detail.
1. Uniform Definition of Wages (Major Impact Area)
Earlier:
Different laws used different definitions of “wages,” therefore causing confusion in PF, bonus, and gratuity calculation.
Now:
- The new codes introduce one standardized definition of wages, where:
- Basic Salary + DA + Retaining Allowance = Wages
- All allowances cannot exceed 50% of the total salary, which includes HRA, overtime, bonus, commission, etc.
Impact:
Companies cannot keep the basic salary too low.
- In many cases, the contribution towards PF, ESI, and gratuity will increase.
- In the long run, it pays employees higher social security.
2. Big Change: Increased Gratuity Benefits
Earlier:
To receive gratuity, employees needed to complete 5 years of continuous service.
Now:
- Gratuities are payable to fixed-term employees without the condition of 5 years, on a pro-rata.
- Contract workers also become eligible under rules.
- More and more workers, temporary or project-based, are granted gratuity benefits.
Impact :
- Improved financial security for temporary workers.
3. Universal Minimum Wage Across India
Earlier:
Minimum wages applied only to certain scheduled industries.
Now:
- The minimum wage applies to all employees in all sectors.
- The Central Government will fix the floor wage, below which no state can set minimum wages.
Impact:
- Uniformity across states
- Better protection of earnings for workers
4. Working Hours May Change (8–12 Hour Flexibility)
Earlier:
8-hour working day was standard, but with state variations.
Now:
- The working hours per day remain 8 hours, while states can permit 12 hours with conditions.
- Maximum weekly hours capped at 48 hours.
- Mandatory rest intervals and maximum spread-over rules apply.
Impact:
- More flexibility for industries.
- Overtime calculation becomes more transparent.
- Employees cannot be exploited by long hours with no proper pay.
5. Overtime Rules Standardized
New Rules:
- Overtime must be paid at double the normal wage.
- Any overtime worked must be documented and approved.
Impacts include
- Workers are adequately compensated for extra hours worked.
- Reduces disputes over overtime payments
6. Leave Encashment & Earned Leave Rules May Change
New Provision:
States may establish standard regulations regarding:
- Earned leave accumulation
- Leave encashment
- Carry forward limits
- Calculation of leave during overtime or night shifts
Impact:
- Employees gain better clarity.
- HR policies are standardized
7. Faster & Modernized Grievance Redressal System
NEW Requirement:
- Companies are required to establish a Grievance Redressal Committee for:
- Resolving employee complaints promptly
- Maintaining harmony in the workplace
Impact:
- Reduced conflict between staff and management.
- Faster resolutions without legal escalation.
8. More Stringent Strike and Lockout Laws
New Provisions:
- Before going on strike, workers must give:
- 14 days notice
- No strike allowed within 60 days of giving notice
- These rules also apply to public utility services like electricity, water, hospitals, etc.
Impact:
- Allows for business continuity
- Reduces abrupt labour stoppages
- Safeguards public interests
9. Permitting Women to Work at Night (With Safety Measures)
New Rules:
- Employed women are now allowed to work between 7 PM and 6 AM, provided employers would supply
- Free transportation
- CCTV & Security Arrangements
- Emergency support
- Consent from the employee
Impact:
- More job opportunities for women
- Ensures safety and equality in the workplace
10. Gig Workers & Platform Workers Get Social Security
For the first time, gig economy workers, such as:
- Zomato delivery partners
- Uber/Ola drivers
- Swiggy delivery staff
- Urban Company workers
- are covered under social security schemes.
They get benefits such as:
- Accident insurance
- Health benefits
- Life insurance
- PF-like schemes (as notified by the government)
Impact:
- Support for millions of self-employed workers
- A key step towards inclusive labour reforms
11. Compulsory Health & Safety Enhancements
Among other things, the OSH Code requires employers to provide the following:
- Clean toilets
- Safe drinking water
- First-aid kits
- Annual medical check-ups, specific sectors
- Safety training for hazardous jobs
Impact:
- Improved working conditions
- Reduced workplace accidents
- Better employee health
12. Easier Recruitment & Laying Off by Employers
New Rule:
Companies employing no more than 300 workers are exempted from government approval on:
- Retrenchment
- Layoffs
- Closing procedures
(The earlier limit was 100 employees.)
Impact:
- Businesses get more flexibility
- Encourages investment
- Faster restructuring during losses
13. Uniform Registration for Migrant Workers
The following will be provided to inter-state migrant workers:
- Travel allowance
- Medical benefits
- Helpline services
- A national registration for benefit tracking
Impact :
- Better protection for migrant labour
- Transparency in worker management
14. Digital Records & Compliance
The new codes encourage:
- Online registers
- Digital attendance
- e-Notices
- Online inspections
Impact:
- Less paperwork for HR
- Reduced corruption Faster compliance checks
15. Business-Friendly Single License System
Companies can get:
- A single license for multiple locations
- One registration for contract labor
- One approval for expanding operations
The Impact:
- Less administrative burden
- Easier expansion for companies
- Encourages MSME growth
Impact of New Labour Law in India on Different Sectors (Expanded)
1. IT & Software Industry
- More WFH flexibility
- Clear overtime rules
- Structured shift hours
- Compulsory appointment letters
IT companies need to revise the HR policies.
2. Retail & Shops
- Attendance by shop owners is compulsory.
- Overtime for festival seasons needs to be paid correctly.
- Safety measures for employees
- Appointment letters even for shop helpers
Small shops today have to behave like organized employers.
3. Manufacturing & Factories
- Strict 48-hour rule
- Higher safety standards
- Health check-ups binding
- Proper leave records required
- Penalties for machine safety violations increased
The factories have to update the compliance ASAP.
4. Hospitals & Clinics
- Better safety facilities for nurses and staff
- Overtime rules apply
- Improved night shift rules for women employees
- Compulsory appointment letters
Healthcare workers are better protected.
5. Education Sector
- Teachers need to have structured working hours.
- Improved salary transparency
- Leaves and appointment letters more compulsory
- Digital attendance recommended
Private schools are now required to maintain adequate HR records.
Benefits of the New Labour Law in India For Women Employees
The New Labour Codes of India—comprising the Wages Code, Industrial Relations Code, Social Security Code, and Occupational Safety & Working Conditions (OSH) Code—bring forth some of the most forward-thinking and women-friendly changes to India’s labor landscape.
These laws are designed to empower women in the workforce, enhance safety measures, and ensure they have equal opportunities without facing discrimination.
1. Women Now Allowed to Work Night Shifts: provided safety measures ensured
This is one of the biggest benefits brought in by the new labour law.
What It Means
Women are now permitted to legally work between 7 PM and 6 AM, provided employers maintain:
- Safe and secure workplace
- CCTV surveillance in work areas
- Free transportation for pickup and drop-off
- Female security staff at night
- Adequate lighting inside & outside the premises
- Emergency response systems
- Written consent of the women employees
Why This Matters
- Expands job opportunities
- Assists women in BPO, IT, healthcare, retail, and logistics industries.
- Promotes gender equality at the workplace
2. Equal Pay and No Sex-Based Discrimination
The New Wage Code categorically states that no employer shall discriminate between men and women in:
- Salary
- Bonuses
- Promotions
- Work assignments
- Hiring or training opportunities
Why This Matters
- Ensures equal pay for equal work
- Protects women from wage gaps or unfair treatment.
- Encourages transparency in wage structures.
3. Improved Maternity Benefits & Job Security
While the laws concerning maternity leave were in place, the revised labour codes provide increased job security and benefits to pregnant employees.
Key Benefits
- Pregnancy: Employers should guarantee a safe work environment.
- No discrimination in promotions or appraisals due to maternity.
- Compulsory medical facilities for female workers in specific workplaces.
- Strict penalties for companies that violate maternity rules.
Why This Matters
- Ensures smooth transition during pregnancy.
- Protects the health and well-being of the mother and child
- Guarantees job continuity and respect for motherhood.
4. Gratuity Eligibility for Fixed-Term Women Employees
Earlier, gratuity was paid to contract workers after 5 years of service.
New Rule
Fixed-term and contract women employees get the following under the Social Security Code:
- Pro-rata gratuity
- No need to complete 5 years
- Benefits even if they work on short-term projects
Why This Matters
- Helps temporarily working women or those working part-time.
- Benefits women who take career breaks due to marriage, maternity, or relocation
5. Safer Workplace & Mandatory Facilities for Women
The OSH Code has made safety rules extremely strict for employers.
- Mandatory facilities include
- Separate, clean women’s washrooms
- Restrooms and seating arrangements
- First-aid kits and medical rooms (for large workplaces)
- Safe drinking water
- Creche facilities (common facility also allowed near workplace)
Why This Matters
- Encourages women to join the workforce.
- Reduces workplace harassment or safety issues
- Ensures hygiene, comfort, and dignity at work
6. Stricter Rules against Sexual Harassment
While the law on POSH is separate, the labour codes integrate safety obligations.
- What Employers Must Ensure
- Functional Internal Complaints Committee (ICC)
- Zero tolerance for harassment
- Complaints treated as confidential
- No victimization or retaliation against complainants
Why This Matters
- Builds trust among female employees
- Ensures emotional and psychological safety
- Promotes a respectful work atmosphere
7. Better rules regarding working hours contribute to an improved work-life balance.
The New Labour Law guarantees that:
- Maximum 8-hour workdays, generally
- Weekly 48-hour limits
- Compulsory break periods
- Permission-based overtime
- Transparent attendance monitoring
Why This Matters
- Reduces burnout
- Supports women who juggle work and family.
- Improves productivity and well-being
8. Social Security Coverage for Women in All Job Types
For the first time, social security benefits cover all types of women workers, including:
- Full-time employees
- Contract workers
- Fixed-term employees
- Gig and platform workers
- Home-based workers
Benefits Include
- PF
- ESI
- Maternity benefits
- Pension schemes
- Accident insurance
Why This Matters
- Ensures financial protection
- Encourages participation in the gig economy
- Supports women entrepreneurs and freelancers
9. More Opportunities in High-Growth Sectors
With night shifts and equal opportunities allowed, women can now work in:
- IT & BPO
- Logistics & warehousing
- Manufacturing units
- Security & facility management
- Retail & malls
- Hotels & restaurants
- Healthcare & emergency services
Why This Matters
- Helps women earn more
- Opens up high-paying roles
- Expands career options previously unavailable to women
10. Encouragement for Women Returning to Work After a Break
The increased flexibility in:
- Fixed-term employment
- Contract roles
- Part-time work
makes it easier for women to return after:
- Pregnancy
- Childcare responsibilities
- Family responsibilities
- Relocation
Why This Matters
- Keeps women’s careers stable.
- Reduces the gap caused by career breaks.
- Encourages more women to rejoin the workforce
New Labour Law in India And Social Security (PF, ESI, Gratuity Explained)
- Contract workers get social security benefits.
- Employers must maintain attendance and working hour records.
- Contractors must provide ID cards.
- Wages must be paid directly into bank accounts.
- Overtime rules apply equally.
Salary Structure Example (Before & After New Labour Law in India)
Old Structure (Take-home higher)
Basic: 30%
HRA: 30%
Special allowance: 40%
New Structure (More social security)
Basic: 50%
HRA: 20–25%
Allowances: 25–30%
Outcome:
- Take-home decreases slightly
- PF, gratuity, retirement security increases
- Salary slips become standardized
How Digital HR Systems Help With New Labour Law in India Compliance
They help in:
- Tracking working hours accurately
- Calculating overtime automatically
- Maintaining payroll logs
- Generating digital attendance reports
- Issuing salary slips
- Storing appointment letters
- Avoiding penalties due to mistakes
Digital systems make compliance simple and fast for all companies.
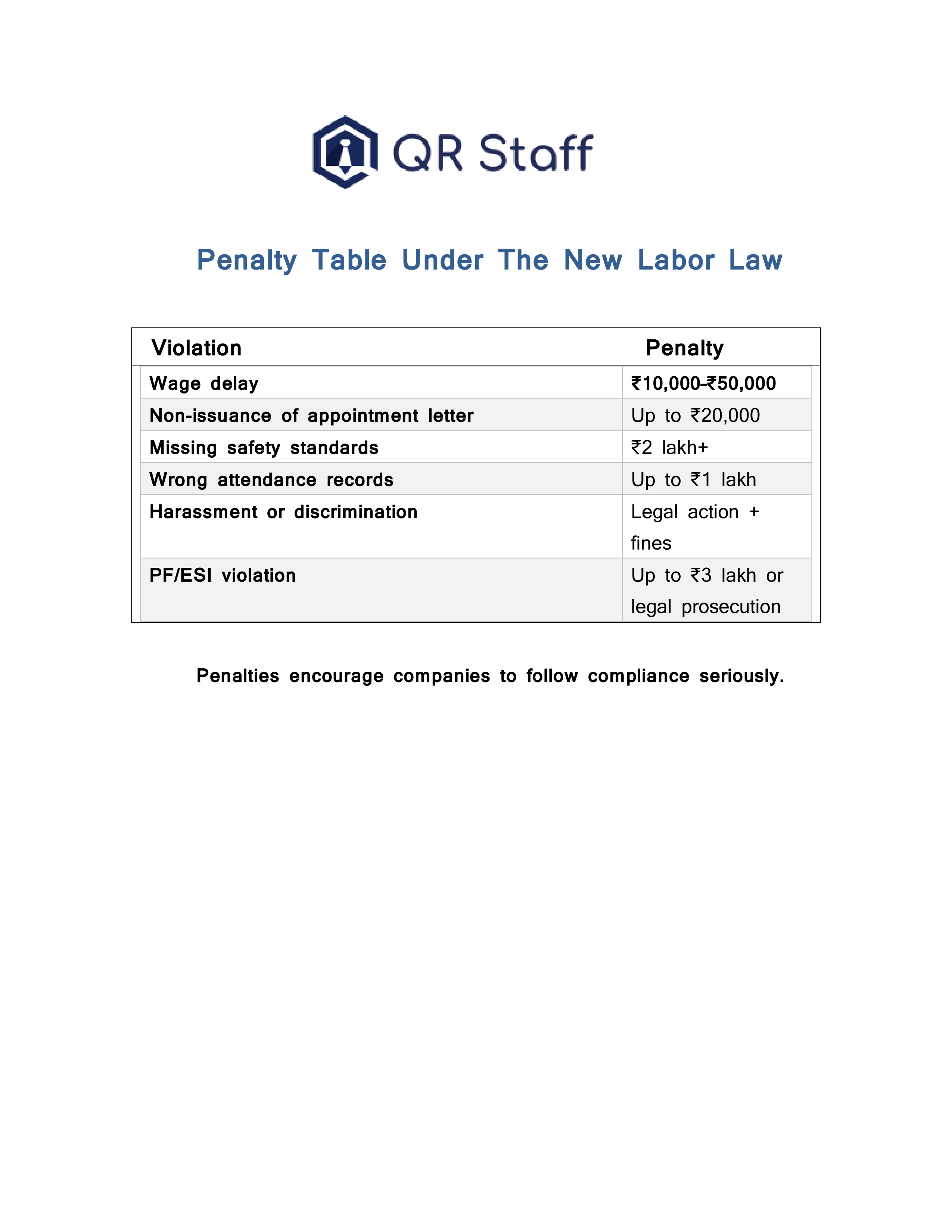
Penalty Table Under The New Labour Law in India
HR Checklist For New Labour Law in India Compliance
HR Must Ensure:
- New appointment letters issued
- Updated salary structure
- 48-hour weekly rule followed
- Overtime tracked digitally
- Annual health check-ups arranged
- Safety guidelines followed
- PF/ESI rules updated
- Digital attendance maintained
- Worker identity records stored
This checklist helps HR stay fully compliant.
Conclusion Of New Labour Law in India
The new Indian labour law ushers in contemporary, employee-friendly, and transparent systems in the workplace. These changes will benefit employers and employees alike by making processes more straightforward, safer, and more organized. Be it wages, safety, HR Full Form or social security, the aim of the reforms is to upgrade India’s manpower resources and guarantee their due consideration. Businesses are required to rework their HR systems, salary structure, and attendance records in order to sustain consistency with the law.
Companies in India require accurate attendance, overtime calculations, digital records, and error-free payroll to smoothly follow the new labour law. QR Staff is a simple, powerful attendance and payroll management app that helps businesses stay 100% compliant. With QR-based attendance, automatic overtime calculation, digital timesheets, and professional salary slips, QR Staff makes HR and payroll easy for shops, clinics, offices, factories, and startups.
Frequently Asked Questions For New Labour Law in India (Expanded)
The latest labour code in India is a set of four laws designed to simplify and modernize the rules for labour. These include the Wage Code, Social Security Code, Industrial Relations Code, and Occupational Safety Code.
Yes, the new labour law makes it compulsory that 50% of the total CTC must be the basic pay, which influences the PF, gratuity, and in-hand salary.
Yes, new legislation permits companies to allow a 4-day workweek, but the limit on weekly hours must remain at 48. If the days of work are reduced, the daily hours will increase accordingly.
In the new regime, there are 4 labour codes. These codes replace 29 old labour laws and make compliance simple.
Under the new labour code, the limit is set at 48 hours per week. Companies may opt for 8-hour, 10-hour, or even 12-hour shifts, as required, but must pay overtime.
New labour rate encompasses a minimum standard rate of wages, PF limit, overtime rates, and 50% basic salary rule under the new Wage Code. Actual rates may be different for different states and industries.
Major changes include:
– 50% salary should constitute basic pay.
– 48-hour weekly limit
– Rules for overtime, leave, and holidays
– Stronger PF & social security
– More transparency for salary slips
– Support for gig and platform workers
The 2025 labour law includes the four new labour codes. It changes wages, working hours, leaves, PF, and compliance rules for all companies to create a fair and organized workplace.
Yes, a 12-hour shift is permissible under the new code as long as the total weekly limit remains 48 hours and overtime pay is given for additional hours beyond regular duty.
